封装
将属性和行为作为一个整体,表现生活中的事物
将属性和行为加以权限控制
访问权限
// 公共权限 类内可以访问,类外可以访问
public:
// 保护权限 类内可以访问,类外不可以访问
protected:
// 私有权限 类内可以访问,类外不可以访问
private:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
long long a, b;
// class代表设计一个类,类后面紧跟着的就是类名称
class Circle
{
// 访问权限
// 公共权限
public:
// 属性
//半径
int m_r;
// 行为
//获取圆的周长
double calculate()
{
return 2*3.14*m_r;
}
};
int main()
{
//通过圆类创建具体的圆
Circle cl;
cl.m_r=10;
cout<<"calculate="<<cl.calculate()<<endl;
return 0;
}
成员属性为私有,可以自己控制读写权限
构造函数
*构造函数,没有返回值,也不写void
*函数名与类名相同
*构造函数可以有参数,因此可以发生重载
*程序在调用对象时会自动调用构造
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
long long a, b;
class Person
{
private:
int m_L, m_W,m_H;
public:
~Person()//函数名和类名相同 在名称前加~
{
cout<<"Person 构造函数的调用"<<endl;
}//构造函数
};
//析构函数 进行清理操作
//构造和析构都是必须有的 自己不提供的话编译器会提供一个空实现的构造和析构
void test1()
{
Person p;//
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}

两种分类方式:
有参构造无参构造
普通构造拷贝构造
拷贝构造函数的调用时机

深拷贝与浅拷贝
浅拷贝:简单的复制拷贝操作
深拷贝:在堆区重新申请空间,进行拷贝操作
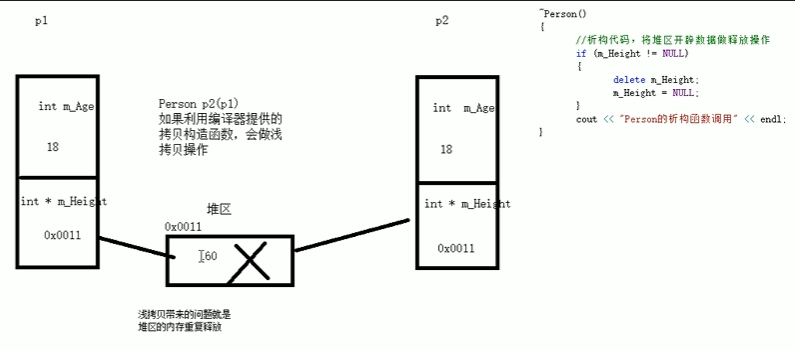
深拷贝【指针】
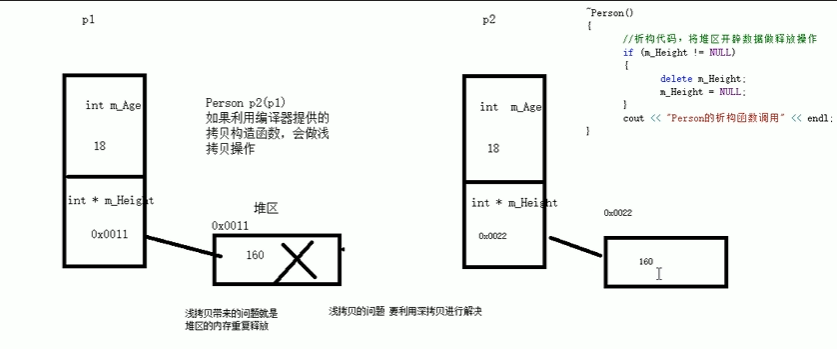
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
int m_age;
int *m_weight;
Person(int age,int weight)
{
m_age = age;
m_weight=new int(weight);
cout << "有参" << endl;
}
Person(const Person &p)
{
cout << "person copydo" << endl;
m_age = p.m_age;
//深拷贝操作
m_weight = new int(*p.m_weight);
}
~Person()
{
if(m_weight!=NULL){
delete m_weight;
m_weight=NULL;
}
cout << "析构do" << endl;
}
};
// 调用
void test01()
{
Person(14,134);
Person p1(19,188);
Person p2(p1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
析构函数
对象的初始化和清理:
初始化列表
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
int m_A;
int m_B;
int m_C;
Person(int a, int b, int c) : m_A(a), m_B(b), m_C(c) {}
};
int main()
{
Person p1(10, 20, 30);
cout << p1.m_A << " " << p1.m_B << ' ' << p1.m_C;
return 0;
}
类对象作为类成员
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Phone
{
public:
string p_kind;
Phone(string name)
{
p_kind = name;
}
~Phone(){
cout<<"析构2"<<endl;
}
};
class Person
{
public:
string m_name;
Phone m_phone;
Person(string name, string kind) : m_name(name), m_phone(kind) {
cout<<"do"<<endl;
}
~Person(){
cout<<"析构1"<<endl;
}
};
void test01()
{
Person p("aisssky", "huawei");
cout<<p.m_phone.p_kind;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
静态成员

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Phone
{
public:
static int m_A;
// 所有成员都共享同一份数据
private:
static int m_B;
};
int Phone ::m_A = 100; // 类外初始化操作
int Phone ::m_B=200;
void test01()
{
Phone p;
Phone p2;
p2.m_A = 200; // 结果变为200
cout << p.m_A << endl;
}
void test02()
{
// 静态成员变量 不属于某个对象上 所有成员都共享一份数据
// 因此静态成员变量有两种访问方式
Phone p3;
// 1.通过对象进行访问
cout << p3.m_A << endl;
// 2.通过类名进行访问
cout << Phone::m_A << endl;//类外访问不到私有成员
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
return 0;
}
静态函数只能访问静态成员
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Phone
{
public:
static int m_A;
// 所有成员都共享同一份数据
static void func(){
m_A=522;
cout<<"static void do"<<endl;
}
private:
static int m_B;
};
int Phone ::m_A = 100; // 类外初始化操作
int Phone ::m_B=200;
void test01()
{
Phone p;
Phone p2;
p2.m_A = 200; // 结果变为200
cout << p.m_A << endl;
Phone::func();
cout << p.m_A << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
对象模型和成员函数分开存储
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Phone
{
};
void test01()
{
Phone p;
cout<<"size of p = "<<sizeof(p)<<endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
//size of p=1
//空对象占用内存为1;
this指针
本质是指针常量 指向是不可以更改的 指向的值是可以修改的
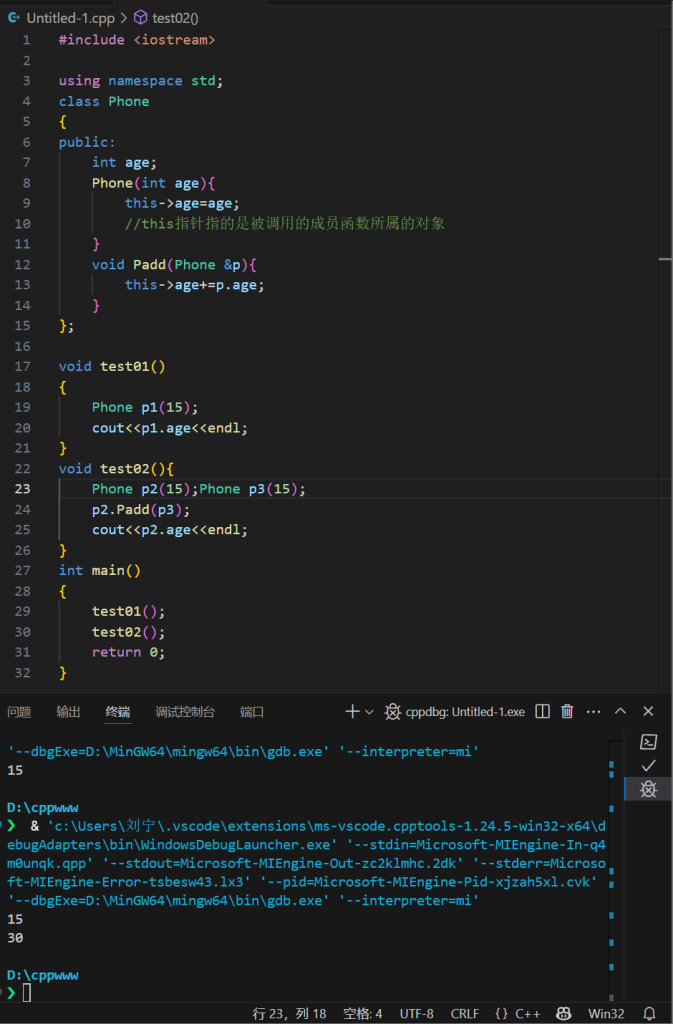
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Phone
{
public:
int age;
Phone(int age){
this->age=age;
//this指针指的是被调用的成员函数所属的对象
}
Phone &Padd(Phone &p){//用引用的方式进行返回
this->age+=p.age;
return *this;//this指向篇p2的指针,*this指向的是p2这个对象的本体
}//返回对象本身
};
void test01()
{
Phone p1(15);
cout<<p1.age<<endl;
}
void test02(){
Phone p2(15);Phone p3(15);
p2.Padd(p3).Padd(p3).Padd(p3);//可以实现追加,就像字符串
cout<<p2.age<<endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
return 0;
}
空指针访问成员函数
如果用到this,需要多考虑if(this==NULL){return;}
void test01()
{
Phone *p=NULL;
Phone p1(15);
p->Show(p1);
cout<<p1.m_age<<endl;
}
const修饰成员函数 加上后 函数为常函数 对象为常对象

在成员函数后面加const修饰的是this指针指向,让指针指向的值也不可以修改
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Phone
{
public:
int m_A;
void show() const//==Phone *const this
{
this->m_B=100;
}
mutable int m_B;//特殊变量 加mutable可以修改
};
void test01()
{
Phone p1;
p1.show();
p1.m_B=250;
cout<<p1.m_B;//250
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
友元
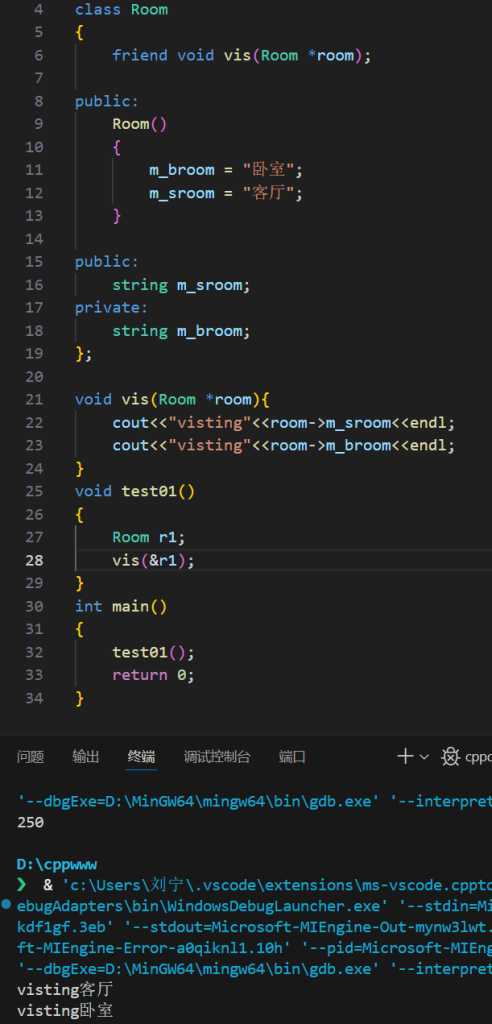
友元类
访问类中的私有成员
成员函数做友元
某类的成员函数作为本类的好朋友,可以访问
运算符重载
1.1加号运算符重载
作用:实现自定义数据类型的运算
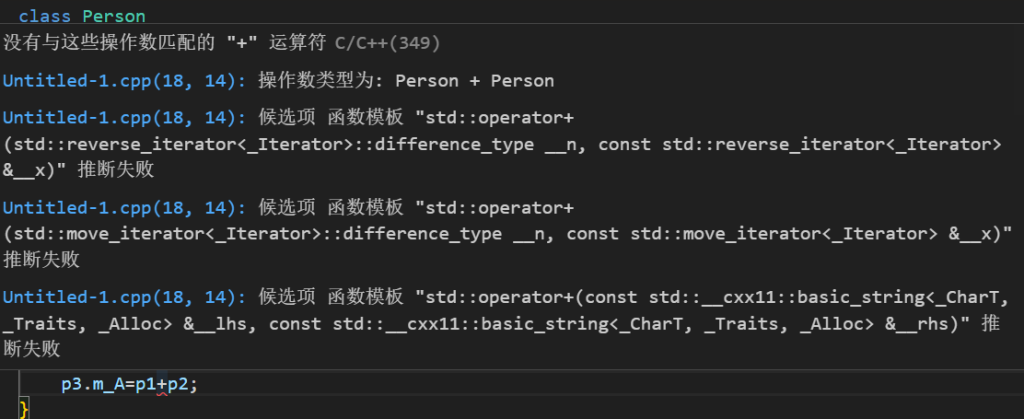
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
int m_A;
int m_B;
Person operator+(Person &p){
Person temp;
temp.m_A=this->m_A+p.m_A;
temp.m_B=this->m_B+p.m_B;
return temp;
}
};
void test01()
{
Person p1;
Person p2;
p1.m_A=10;
p1.m_B=12;
p2.m_A=10;
p2.m_B=13;
Person p3;
p3=p1+p2;
cout<<p3.m_A<<endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
1.2左移运算符
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
int m_A;
int m_B;
};
ostream &operator<<(ostream &cout,Person &p){
cout<<p.m_A<<endl;
cout<<p.m_B<<endl;
return cout;
}
void test01()
{
Person p1;
p1.m_A=10;
p1.m_B=12;
cout<<p1<<"aisss"<<endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}1.3递增运算符重载
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Myint
{
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &cout, Myint myyint);
public:
Myint()
{
m_num=0;
}
Myint &operator++(){
m_num++;//进行++运算
return *this;//返回自身,*this
}
Myint operator++(int){//后置++运算符重载,int为占位参数,double等其他不好使
//先记录结果
Myint temp=*this;
//递增
m_num++;
//返回记录结果
return temp;
}
private:
int m_num;
};
//重载<<
ostream &operator<<(ostream &cout, Myint myyint)
{
cout<<myyint.m_num;
return cout;
}
void test01()
{
Myint p;
cout<<++(++p)<<endl;
//cout<<p<<endl;
}
void test02()
{
Myint mml;
cout<<mml++<<endl;
cout<<mml<<endl;
}
int main()
{
int a=0;
cout<<++a<<endl;
test01();
test02();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
1
2
0
1
赋值操作
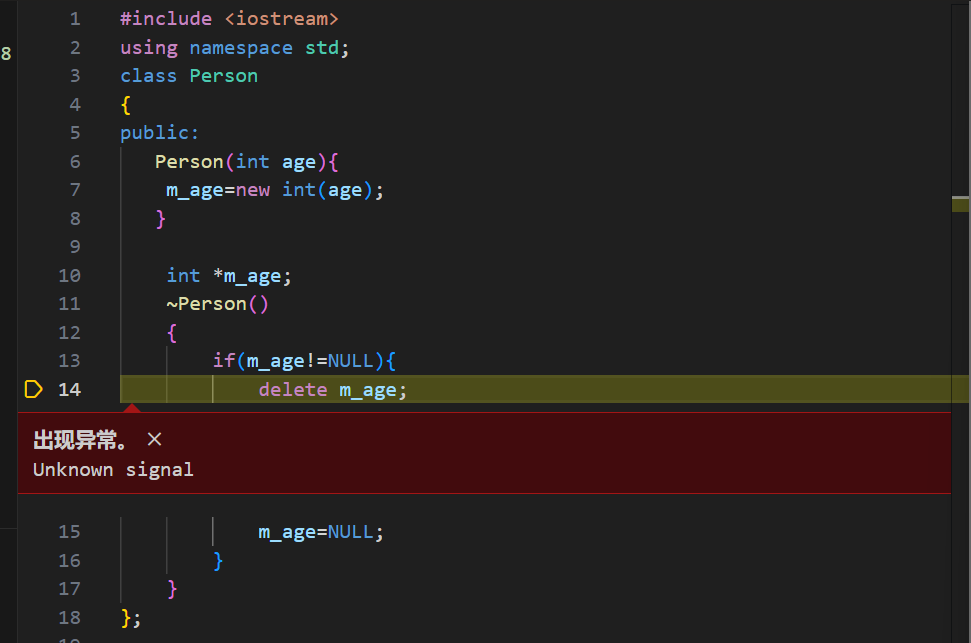
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person(int age){
m_age=new int(age);
}
int *m_age;
~Person()
{
if(m_age!=NULL){
delete m_age;
m_age=NULL;
}
}
Person &operator=(Person &p)
{
//先判断是否有属性在堆区,如果有先释放干净,
if(m_age!=NULL){
delete m_age;
m_age=NULL;
}
//再深拷贝
m_age=new int(*p.m_age);
return *this;
}
};
void test01()
{
Person p1(18);
Person p2(20);
Person p3(26);
p2=p1=p3;//实现赋值的连等,需要返回自身
cout<<*p1.m_age<<endl;
cout<<*p2.m_age<<endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
重载关系运算符
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age){
m_name=name;
m_age=age;
}
string m_name;
int m_age;
// 重载关系运算符
bool operator==(Person &p)
{
if (this->m_name == p.m_name && this->m_age == p.m_age)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool operator!=(Person &p){
if(this->m_name!=p.m_name||this->m_age!=p.m_age){
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool operator>=(Person &p){
if(this->m_age>=p.m_age){
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
void test01()
{
Person p1("aisssky", 18);
Person p2("aisssky", 18);
if(p1==p2){
cout<<"iwc"<<"磕你俩了"<<endl;
}
else if(p1!=p2){
cout<<"唉"<<endl<<"没关系"<<endl;
if(p1>=p2){
cout<<"那p1在左边吧"<<endl;
}
else{
cout<<"那p2在左边吧"<<endl;
}
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
函数调用重载(仿函数)非常灵活,没有固定的写法,类似于平时调用的函数库写法
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
void operator()(string name){
cout<<name<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Person MyPrint;
MyPrint("gogogo");
return 0;
}